TL;DR: The Evolution of SaaS Pricing
The global SaaS market is rapidly abandoning rigid subscription models in favor of Value-Based Pricing (VBP). The most significant shift involves adopting Hybrid Models (subscription + usage) and pure Usage-Based Pricing (UBP), which currently drive the highest median growth rates (21%). Success requires selecting a Value Metric that aligns directly with customer outcomes, implementing a robust technical stack for real-time metering, and ensuring absolute transparency to prevent "bill shock." The future will transition toward AI-powered, Outcome-Based Pricing.
Who This Is For
This guide serves SaaS founders, Product Managers, and CFOs who must structure pricing to ensure customer value aligns perfectly with revenue growth. In a market projected to exceed $1 trillion by 2032, no strategic lever proves more critical than pricing.
The global SaaS market is a $317 billion financial powerhouse. For decades, the fixed, recurring fee model served as the industry standard. However, the pure subscription model presents inherent limitations: customers face the pain point of paying for underutilized "shelfware," while vendors struggle to capture value from high-consumption users. This dynamic drives a necessary evolution.
This definitive guide breaks down the three primary SaaS pricing models—Subscription, Tiered, and Usage-Based—compares their strategic and technical implications, and forecasts a future where hybrid and outcome-based pricing dominate the trillion-dollar landscape.
1. The Shifting Landscape of SaaS Pricing
The Dominance of Value-Based Pricing
A fundamental shift is underway: companies no longer determine pricing by cost-plus (cost of production + margin) or competitor analysis. Pricing is now overwhelmingly driven by the Value-Based Pricing (VBP) model. VBP means charging based on the perceived value a customer receives from the product, not its operational cost.
A staggering 78% of surveyed companies primarily implement this Value-Based Pricing strategy, highlighting a definitive movement away from traditional, outdated methods.
Statistics Driving the Change
The market rapidly internalizes this value alignment, demonstrated by the sharp decline in reliance on pure subscription models and the parallel surge in consumption-based billing:
- UBP Trend: Adoption of Usage-Based Pricing (UBP) has increased by 31% since 2023.
- Subscription Decline: The use of pure subscription models has dropped from 65% to 43% in the same period.
The most successful approach today blends the stability of subscriptions with the scalability of usage metrics.
📈 The Power of Hybrid Models
Companies using hybrid pricing models (combining a base subscription fee with a usage component) report the highest median growth rate (21%) in the industry. This structure maximizes both predictable revenue and high Net Revenue Retention (NRR).
Customer Pain Points Demand Flexibility
The core financial pain point for customers is a mismatch between money paid and value received—a problem exacerbated by rigid pricing structures. This user-centric pressure forces vendors to introduce flexibility:
- Flexibility Demand: 81.2% of businesses surveyed report that the inability to provide flexible payment options directly hinders closing deals.
This demand sets the stage for a deeper look into the mechanics of the three primary pricing models.
2. Definitive Breakdown of the Core Pricing Models
2.1. Subscription Model: The Foundation
- Mechanism and Simplicity
- Customers pay a fixed, recurring fee (monthly or annually) for software access, regardless of actual consumption. This simplicity is its primary strength.
- Vendor Benefit
- Provides the steadiest and most predictable revenue stream, essential for accurate financial forecasting and securing investor confidence.
- Customer Experience Trade-offs
-
- Benefit: Simple; customers easily budget and forecast costs.
- Pain Point: High risk of "shelfware" or overpaying for underutilized services, leading to a perception of poor value and eventual churn.
2.2. Tiered Pricing Model: The Classic Upgrade Path
- Mechanism and Segmentation
- The Tiered model offers a range of fixed-price packages (e.g., Basic, Pro, Enterprise). Differentiation typically relies on three elements: features, user count, or usage allowances/caps.
- Strategic Advantage (Upselling)
- This model excels at market segmentation. It caters to different customer sizes and budgets, providing a clear, natural upgrade path (upsell opportunity) as a customer’s business grows.
- Customer Experience Trade-offs
-
- Benefit: Offers choice and flexibility, allowing customers to select the package that best fits their immediate needs.
- Pain Point: Customers often face dissatisfaction if desired features are locked in a much higher, expensive tier, or if they struggle to differentiate the true value between packages. Simplified tiers (3–4 options) work better than 5+ options.
| Tier | Monthly Price | Primary Differentiation | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Basic | $49 | Core features, 1-5 users, 1,000 API calls/month | Startups, Small Teams |
| Pro | $199 | Advanced features, unlimited users, 10,000 API calls/month | Scaling Businesses |
| Enterprise | Custom | All features, dedicated support, custom usage/SLA | Large Corporations |
2.3. Usage-Based Pricing (UBP): The Fairness Model
- Mechanism and Value Alignment
- Customers are charged based on the actual amount of service consumed, measured by a specific Value Metric. Revenue scales perfectly with a customer's usage, ensuring direct alignment between the vendor's success and the customer's success.
- Vendor Benefit
- Revenue scales perfectly with product adoption. Vendors capture high revenue from high-value, high-consumption customers while maintaining a low barrier to entry for smaller users.
- The Crucial Value Metric
- This is the most important technical decision. The metric must align with the customer’s perceived value. Actionable advice: Choose a metric that indicates value delivery (e.g., "successful messages delivered with engagement") rather than a simple operational metric (e.g., "number of contacts stored").
- Customer Experience Trade-offs
-
- Benefit: Fairness, a pay-as-you-go structure, and a low barrier to entry for new customers.
- Pain Point: Significant risk of "surprise overages" or "bill shock" from unexpected usage spikes, which makes budgeting difficult and quickly erodes trust.
3. Technical Requirements and Best Practices for Implementation
3.1. Building a Modern UBP Infrastructure
A robust technical stack is non-negotiable for any advanced pricing model, especially UBP. Companies cannot implement Usage-Based Pricing effectively or transparently without the right infrastructure.
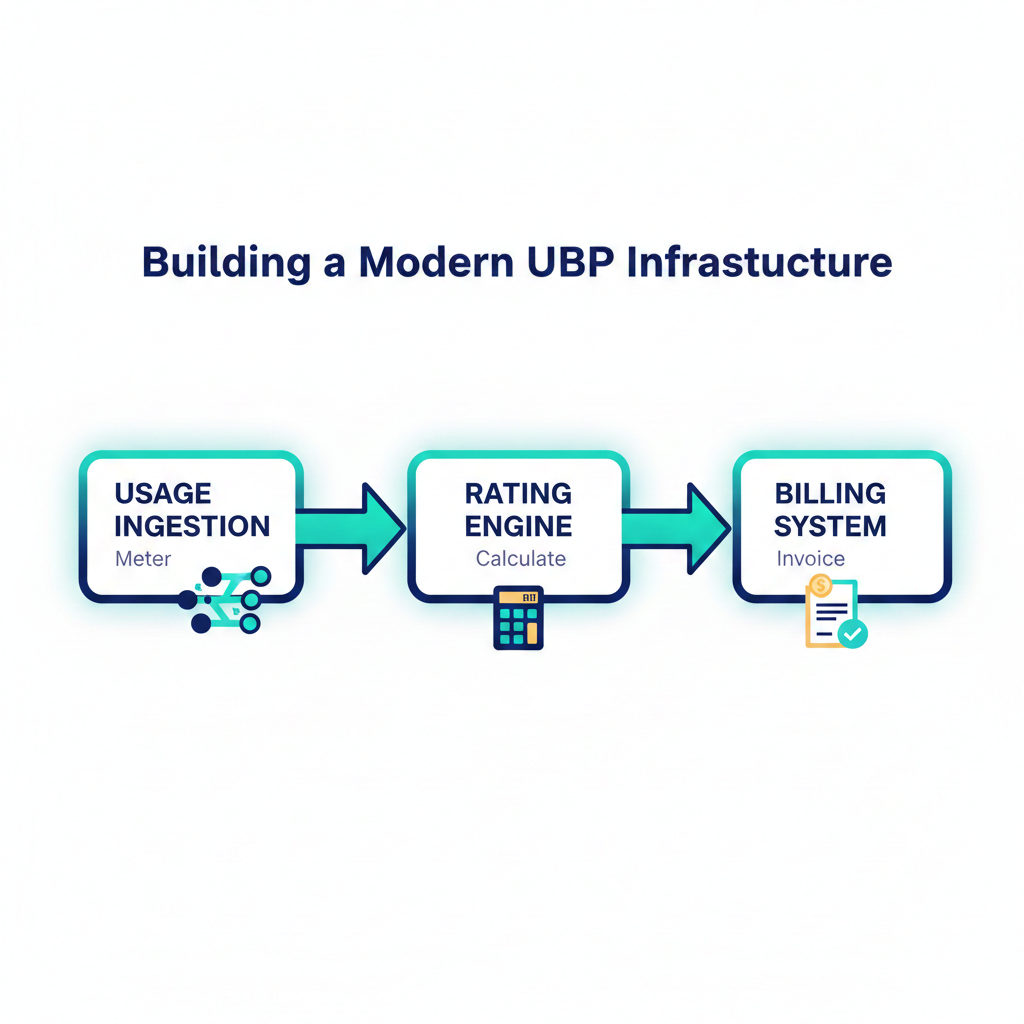
The core components of a modern UBP and SaaS billing system are:
- Usage Ingestion (Metering): This engine captures high-volume usage data in real-time. It must be robust, scalable, and capable of maintaining clean, reliable records (e.g., de-duplication, handling data velocity) to ensure accurate billing.
- Rating Engine: This logic layer takes the metered data and applies the pricing model. It defines the metered features, applies flexible rating models (flat rates, tiers, thresholds, overages), and calculates the final charge for each customer.
- Automation: Modern pricing and billing systems automate complex logic (e.g., overage calculations, dynamic tier changes) and ensure compliance with stringent accounting standards (e.g., revenue recognition standards like ASC 606).
3.2. Strategic Best Practices for All Models
Transparency and Communication
Complexity and ambiguity breed mistrust. To combat the fear of bill shock and overpayment, two rules are paramount:
- Clarity: Clearly define what each price includes, what the overage thresholds are, and what the Value Metric measures.
- Communication: Communicate all price changes transparently with ample advance notice and a clear explanation of the value increase. (SaaS subscriptions and services have, on average, become nearly 9% more expensive compared to the previous year.)
Simplicity and Data-Driven Refinement
Your pricing must be easy to understand at a glance. Furthermore, companies must treat it as a living, dynamic strategy, not a static fixture:
- Simplicity: Keep the structure accessible. Simplified tiers (ideally 3–4 options) consistently show better performance metrics than overly complex structures with 5+ options.
- Data-Driven: Continuously analyze customer usage data (through cohort analysis) and product adoption metrics. This data drives informed pricing strategy and continuous refinement of tiers, features, and limits.
4. The Future of SaaS Pricing: Hybrid and Outcome-Driven
Hybrid Models as the Standard
The transition is already underway: Hybrid Pricing is poised to become the new standard. By 2025, over 60% of SaaS providers are expected to offer some form of consumption-based option. The combination of a stable base subscription fee plus a scalable usage component mitigates the risk of unpredictable revenue while ensuring that high-growth customers pay their fair share.
AI and Outcome-Based Pricing
The most transformative trend on the horizon, especially for AI-native SaaS and generative AI tools, is the shift toward Outcome-Based Pricing. This model takes the Value-Based principle to its ultimate conclusion:
- Definition: Pricing is tied directly to a measurable business outcome (e.g., revenue generated from a campaign, successful task completion, or customer retention lift) rather than just features or user seats.
- Impact: Outcome-Based Pricing fundamentally removes the divide between vendor and customer success, as the vendor only gets paid when the customer demonstrably achieves their goal.
AI-Powered Optimization
As pricing complexity increases, the sophistication of the tools managing it must also increase. AI-powered pricing optimization tools are projected to increase profitability by up to 30% by 2025 by enabling real-time adjustment of pricing based on current usage, shifting market conditions, and a customer’s willingness to pay. This dynamic approach represents the final frontier in maximizing value capture.
Our Verdict: Key Takeaways
For any SaaS leader looking to future-proof their revenue model, the following points must guide your strategy:
- Value is King: The core of modern pricing is aligning cost with customer-perceived value (Value-Based Pricing).
- Hybrid is the High-Growth Model: While Usage-Based Pricing (UBP) is trending, the combination of a base subscription and a usage component (Hybrid) currently delivers the best median growth (21%).
- Technical Investment is Mandatory: Implementing UBP or hybrid models demands a robust technical stack for real-time metering, a sophisticated rating engine, and automated billing to ensure accuracy and compliance.
- Transparency is Non-Negotiable: To avoid "bill shock" and subsequent churn, be absolutely transparent about your Value Metric, usage thresholds, and any price changes.
The era of rigid, one-size-fits-all pricing is over. Auditing your current model for value alignment and planning the necessary technical stack for a hybrid transition is the most critical step you can take today to secure your slice of the trillion-dollar market of tomorrow.



